Zhamalov A.Zh,
Kunelbayev M.M, Bekarystanova N.S.
Kazakh State Woman Pedagogical University
The Republic of Kazakhstan,
Almaty
RESOURCES OF
RECEPTION OF BIOGAS IN THE REPUBLIC OF KAZAKHSTAN
Abstract
The most suitable raw materials for biogas reception
is manure of pets and the bird's dung. Can be used and other agricultural
waste, such, as the straw used in quality on-line deleted from residential
buildings, an organic waste of food manufactures, a waste of public catering
establishments and deposits (øëàìû) sewage of sewer treatment facilities.
Animal industries waste is of
interest from the point of view of their use for reception of biogas and ýíåðãèé only in the event that
animals are concentrated in the closed premises. In this case there is a
possibility of economically defensible gathering of manure with minimum or ïîèëüíûì absence
of mud impurity. A considerable quantity of the dirt which is present at
manure, leads to sharp decrease in an exit at bio gas fiction.
Liquid manure moves in ìåòàíòàíê, a mix of firm manure with dry organic íàïîëíèòåëåì (straw and ò.ï) – in fermented, and air - with the help âîçäóõîäóâêè. At the expense of biochemical
oxidation at temperature 50-600ñ there is a process àíàýðîáíîãî ñáðàæèâàíèÿ manure - biogas allocation.
Thus, in the conditions of Kazakhstan where the greatest distribution
was received by system of the maintenance of animals, at definition of total of
manure, suitable for processing, it is necessary to take in calculation time of
the maintenance of animals in the closed premises. For pigs and a bird it is
time will equal to 365 days since these animals all-the-year-round contain in
the closed premises. For a horned cattle this time in Southern region can be
accepted to equal 200 days.
The table
Potential possibilities of manufacture of biogas from manure of animals
|
Animals |
Manure exit From 1 Animal, |
Including The dry The organic Substances Manure, êg/day |
Exit of biogas from 1 kg, organic Substances of manure, |
Maintenance time indoors or in night rest of animals, in a year |
Livestock of animals, thousand goals |
|
Horned cattle |
38,5 |
6,0 |
0,34 |
200 |
2117 |
|
Sheep and goats |
3,0 |
1,0 |
0,25 |
120 |
5239 |
|
Pigs |
5,0 |
0,9 |
0,30 |
365 |
562 |
|
Bird |
0,7 |
0,27 |
0,40 |
365 |
10565 |
|
Horse |
25,0 |
4,0 |
0,56 |
60 |
495 |
|
Camels |
40,0 |
7,0 |
0,4 |
120 |
52 |
Results of calculations by
definition of an exit of manure and biogas from the specified livestock of
animals of Republic Kazakhstan are shown in table (2,4,5). At definition of an
exit of manure it was considered that manure from ÊÐÑ on îòêîðìå cannot be used because
of the high maintenance of a dirt and the earth.
As a result of technology application àíàýðîáíîãî ñáðàæèâàíèÿ horned cattle manure (ÊÐÑ) with reception of biogas, organic fertilizers, protein fodder additives
the following positive effect turns out.
Apparently from òàáëèöà4, except the economic benefit connected in reception from an organic
waste, high-quality gaseous fuel, a fodder protein and organic fertilizer,
takes place obviously expressed ecological at the expense of decrease in
pollution of atmosphere of water and soil.
Table 2
Positive effect of
reception of biogas from manure
|
¹ ï/ò |
Positive effect |
Quantitative
characteristics |
|
1 |
Biogas reception |
Gas make 0,03-0,04 ì3 on 1 kg of dry organic weight (0,3 ò.ó.ò. On 1 conditional
head ÊÐÑ) |
|
2 |
Decrease in biological contamination of water and soil |
Decrease in pollution of sewage on 70-90 % |
|
3 |
Destruction of seeds of weeds in manure |
Reduction of losses grain on 4-5 ts/hectares at the expense of reduction
of losses of nitrogen (140kg/hectare), phosphate (30kg/hectare) on a food |
|
4 |
Increase of value of biological fertilizer |
Decrease in losses of nitrogen of 20 %, increase of biological activity
of nitric connections, productivity increase on 8-12 % |
|
5 |
Protein reception |
Reception on 1 conditional head ÊÐÑ 1 ò a vitamin concentrate in a year (0,15 kg of pure vitamin Â12) enriched 300 ò forages |
|
6 |
Decrease in harmful emissions in atmosphere |
At the expense of replacement by biogas of the firm and liquid harmful
emissions, effect decrease for 1 Gkal of warmth at replacement of firm fuel
of 14-16 thousand rbl. liquid - 1,4 thousand rbl. a year |
Application of technology and àíàýðîáíîãî ñáðàæèâàíèÿ manure with
reception of biogas and organic fertilizers will be rather effective in any the
farmer and country economy removed from centralised systems of power supply.
|
Potential exit of biogas, thousand ì3 |
||||||||
|
Across Kazakhstan |
1751748 |
314355 |
110704 |
832930 |
132988 |
34848 |
3177573 |
|
|
Across the western Kazakhstan |
317383 |
60111 |
10917 |
43099 |
33062 |
21806 |
486378 |
|
|
The potential quantity of energy developed from manure of animals for
year: |
||||||||
|
Kazakhstan |
||||||||
|
Electric energy, billion êWt*t |
10,76 |
1,93 |
0,68 |
0,51 |
0,05 |
0,03 |
13,970 |
|
|
Thermal energy, thousand GDzh |
38173 |
6948 |
2448 |
1836 |
188 |
77 |
50,310 |
|
|
The western
Kazakhstan |
||||||||
|
Electric energy, billion êWt*÷ |
1948,7 |
369,0 |
67,0 |
264,6 |
203,0 |
13,4 |
2865,1 |
|
|
Thermal energy, thousand GDzh |
7014 |
1328 |
241 |
952 |
730 |
48 |
10313 |
|
It is necessary to notice that for
Republic Kazakhstan the basic biogas potential is created by two kinds of
animals, sheep and a dung of a bird, and for the Western Kazakhstan of region -
only sheep.
From table 4 it is possible to
conclude that first of all biogas can be used in five areas - Almaty,
JU-Kazakhstan, V-Kazakhstan, Aktyubinsk and Zhambylsky where the big share of
animal industries is concentrated.
Table 4
Power equivalent of biogas potential
from manure of animals and a dung of birds on areas of Kazakhstan in 2001.
Million êVò*t.
|
Areas |
Kinds of
animals |
Power equivalent |
||||||
|
Largely horned livestock |
Sheep and goats |
Pigs |
Birds |
Horses |
Camels |
Energy |
Thermal energy.ÃDzh |
|
|
Acmolinsk |
902 |
36,8 |
108,5 |
68,7 |
3,5 |
0,3 |
1119,8 |
47,81 |
|
Akyubinsk |
801 |
125,8 |
46,4 |
16,2 |
7,6 |
2,9 |
999,9 |
3600,8 |
|
Almaty |
1227 |
411,3 |
73,4 |
43,6 |
7,5 |
1 |
1763,6 |
6349 |
|
Anyrau |
268 |
69,3 |
- |
1,2 |
1,4 |
2,5 |
342,4 |
1232,6 |
|
Vostok |
1297 |
227,3 |
61,3 |
78,5 |
5,2 |
- |
1669,4 |
6013,7 |
|
Zhambyl |
802 |
238,7 |
27,2 |
35,8 |
2,5 |
0,9 |
1107,1 |
3987 |
|
West
Kazakhstan |
862 |
108,3 |
19,6 |
10,7 |
2,3 |
0,9 |
1100,1 |
3962,9 |
|
Karaganda |
819 |
121,7 |
47,4 |
53,8 |
5,9 |
2,1 |
1049,9 |
3779,6 |
|
Kostanai |
925 |
38,2 |
135,2 |
84 |
2,8 |
- |
1185,2 |
4269,4 |
|
Kyzylorda |
410 |
101,1 |
10 |
9,3 |
2,2 |
6,1 |
538,6 |
1940,2 |
|
Mangystau |
15 |
66,3 |
- |
0,9 |
1,4 |
7,6 |
91,2 |
328,5 |
|
Pavlodar |
646 |
37,3 |
33,7 |
20,7 |
2,2 |
- |
739,9 |
2665,3 |
|
South
Kazakhstan |
754 |
24,6 |
105,7 |
40,4 |
3 |
- |
927,7 |
3341,8 |
|
North
Kazakhstan |
1032 |
373,1 |
11,6 |
32,1 |
4,3 |
2,3 |
1683,1 |
6058,1 |
|
Total |
10760 |
1930,5 |
679,8 |
570,9 |
51,8 |
26,6 |
13970 |
50310,4 |
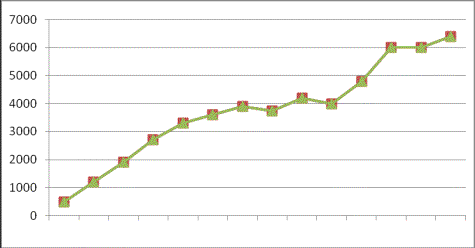
Fig. 2. Annual power an
equivalent biogas potential from manure of areas of Kazakhstan

Fig. 3. Annual ýíåðãè÷åñêèé an equivalent of biogas potential from manure in Southern Kazakhstan
Thus, calculations by quantity of biogas which can be received from manure
of pets and the bird's dung for Republic Kazakhstan allow to receive value
13,970mlrd.kVt*ch/year.
Conclusion
Biogas resources make 79,4 million GDZH/YEAR. The biogas received from
manure, can be used for independent heat - and electrical supplies of farms.
The biogas received from the bird's dung can be used for power supply of
several integrated poultry farms. From a firm waste it is possible to receive
biogas for gas supply of the small enterprises, and also for heat - and
electrical supplies of sewer treatment facilities.
Ëèòåðàòóðà
1.Øèøêèí Í.Ä. Ñèñòåìû
àâòîíîìíîãî òåïëî è ýëåêòðîñíàáæåíèÿ ôåðìåðñêèõ õîçÿéñòâ ñ èñïîëüçîâàíèåì
íåòðàäèöèîííûõ âîçîáíîâëÿåìûõ èñòî÷íèêîâ ýíåðãèè. Èçâåñòèÿ ÀÏÅ ¹1 81-84 ñ.
2. Äåíèñåíêî Ã.È.
Âîçîáíîâëÿåìûå èñòî÷íèêè ýíåðãèè. Êèåâ. 1986-148 ñ.
3. Äàôôè Äæ., Áåêìàí Ó.
Òåïëîâûå ïðîöåññû ñ èñïîëüçîâàíèåì ñîëíå÷íîé ýíåðãèè.Ì.Ìèð 1977.-420ñ.
4. Ñåéòêóðáàíîâ è äð.
Ïðîáëåìû èñïîëüçîâàíèÿ ýíåðãèè ñîëíöà, âåòðà è áèîìàññû 1991.¹2. 36-44 ñ.
5. Ïàíöõàâà Å.Ñ. Áèîãàçîâûå
òåõíîëîãèè è ðåøåíèå ïðîáëåì áèîìàññû
«Ïàðíèêîâîãî ýôôåêòà Ðîññèè». Òåïëîýíåðãåòèêà. 1999.¹2. 30-39 ñ.