Ñîâðåìåííûå èíôîðìàöèîííûå òåõíîëîãèè/1. Êîìïüþòåðíàÿ èíæåíåðèÿ
cand. tech. sci. Semakhin A.M.
Kurgan State University,
Russia
RESERVES
OF TIME OF NETWORK MODEL OF INFORMATION SYSTEM
Creation of corporate information system
demands performance of great volumes of works with high probability of
observance of the set terms of realization and precise coordination of
interaction of executors/1/.
Effective way of representation and
management of a complex of the interconnected works are methods of network
planning/2/.
The analysis of network model is carried out
for revealing reserves of time. Reserves of time have noncritical ways of the
network schedule. The reserve of time shows on how many duration of all
noncritical works/3/can be increased.
Reserves of time are subdivided into
following kinds: a full reserve, a private reserve of the first kind, the free
reserve, an independent reserve.
The full reserve shows on how many it is
possible to increase duration of noncritical work provided that term of
performance of the project will not change. The full reserve of an operating
time (i, j) pays off under the formula
![]() , (1)
, (1)
where ![]() -
late term of fulfilment j events;
-
late term of fulfilment j events;
![]() -
early term of fulfilment i events;
-
early term of fulfilment i events;
![]() -
duration of performance of work i - j;
-
duration of performance of work i - j;
i - the previous event;
j - the subsequent event.
The private reserve of the first kind is a
part of a full reserve on which it is possible to increase operation time, not
having changed late term of initial event. The private reserve of the first
kind pays off under the formula
![]() , (2)
, (2)
where ![]() -
late term of fulfilment j events;
-
late term of fulfilment j events;
![]() -
late term of fulfilment i events.
-
late term of fulfilment i events.
Free reserve - a part of a full reserve by
which it is possible to increase operation time, not having changed early term
of final event. The free reserve of an operating time (i, j) pays off under the
formula
![]() , (3)
, (3)
where ![]() -
early term of fulfilment j events;
-
early term of fulfilment j events;
![]() -
early term of fulfilment i events.
-
early term of fulfilment i events.
The independent reserve of time is a part of
a full reserve which remains if all previous works come to an end in late
terms, and the subsequent works begin in early terms. The independent reserve
of an operating time (i, j) pays off under the formula
![]() , (4)
, (4)
where ![]() -
early term of fulfilment j events;
-
early term of fulfilment j events;
![]() -
late term of fulfilment i events;
-
late term of fulfilment i events;
The degree of complexity of performance of
work of a noncritical way to the set term is defined by factor of intensity
under the formula
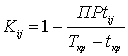 (5)
(5)
where ![]() - a
full reserve of an operating time (i, j);
- a
full reserve of an operating time (i, j);
![]() -
length of a critical way;
-
length of a critical way;
![]() -
duration of a part of the maximal full way containing work i-j which coincides
with critical by.
-
duration of a part of the maximal full way containing work i-j which coincides
with critical by.
The more close the factor of intensity to
unit, the is more complex to perform the given work in target dates /2, 3/.
The network model of creation of corporate
information system of the District Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund of
Kurgan region is developed. The network schedule of
performance of works, length of a critical way and topology are certain.
Factors of intensity and reserves of time are calculated. Optimization of the
network schedule and forecasting of performance of works with a high degree of
probability is lead. Network modelling has allowed to plan and execute
effectively a complex of works on creation of corporate information system with
the least expenses and in the set terms.
Presence of reserves of time allows to carry
out optimization of the network schedule, flexibly to operate a complex of works
by means of redistribution of resources.
References:
1. Broydo V.L. Computing system, networks and
telecommunications: the Textbook for high schools. - SP.: Peter, 2005. - 703 p.
2. Formin G. P.. Mathematical Methods And Models In
Commercial Activities.: Textbook – M.: Finansy I Statistika, 2001. – 544 p.
3. Kochkina E.M., Radkovskaya E.V. Methods Of
Research And Modelling Of National Economy. - Ekaterinburg, Publishing house
Ural State Economic University, 2001. - 93 p.