Grechikho M.
Bukovyna State Financy Academy
The elements
of marketing and their relationships
There are many different definitions of marketing. Let’s
consider some of the following alternative definitions:
“The all-embracing function
that links the business with customer needs and wants in order to get the right
product to the right place at the right time”.
“The achievement of corporate
goals through meeting and exceeding customer needs better than the competition”.
“The management process that identifies
anticipates and supplies customer requirements efficiently and profitably”.
“Marketing may be defined as
a set of human activities directed at facilitating and consummating exchanges”.
All these definitions are right and they try to embody the essence of
marketing:
-
Marketing is about meeting the needs and wants of customers;
-
Marketing is a business-wide function – it is not something that
operates alone from other business activities;
-
Marketing is about understanding customers and finding
ways to provide products or services which customers demand.
The following diagram summarizes the key elements of marketing and their
relationships [2].
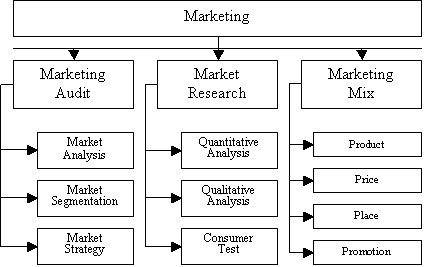 Marketing research,
as a sub-set aspect of marketing activities, can be divided into the following
parts:
Marketing research,
as a sub-set aspect of marketing activities, can be divided into the following
parts:
-
Primary research (also known as field research), which involves the
conduction and compilation of research for a specific purpose.
-
Secondary research (also referred to as desk research), initially
conducted for one purpose, but often used to support another purpose or end
goal.
There also exist additional modes of marketing research, which are:
-
Exploratory research, pertaining to research that investigates an
assumption.
-
Descriptive research, which, as the term suggests, describes "what
is".
-
Predictive research, meaning research conducted to predict a future
occurrence.
-
Conclusive research, for the purpose of deriving a conclusion via a
research process [3].
A marketing audit is a comprehensive, systematic, independent and
periodic evaluation of a company's marketing assets. It is an effective tool in
reviewing the competence of a marketing strategy, analyzing the objectives,
policies and strategies of the company's marketing department as well as the
manner and the means employed in attaining these goals.
Because of the constantly varying business environment, marketing audit
is frequently required, not only at the beginning of the planning process, but
along with the implementation stage, providing also ground for evaluating
possible future courses of action.
Marketing audit on a regular basis is a strong reference point,
reflecting evolution in external business environment, internal experience and
strategy development.
The marketing audit focuses on
three key headings:
§
The external marketing
environment
§
The internal marketing
environment
§
Evaluation on the current marketing plan
External environment consists
of economic, political and legal factors and concentrates on clients and
competition.
Marketing audit of the external surroundings analyses the customers,
their needs and how to meet them, their behavior and decisions, perception of
products and brands, segmentation, targeting and positioning on the market. The
nature of competition is also studied, concerning its concentration,
profitability, strengths and weaknesses, plans and strategies. New entrants on
the market are also studied as well as the substitute products, the influence
of supplier [3].
The cultural nature of the external environment consists of education
levels and standards, religion and beliefs, as well as lifestyle and customs.
Demography plays a key role in marketing audit of the consumers, reflecting on
growth distribution, age, evolution of technology and information systems as
well as marketing communication and media. The external economic conditions
consist of indicators as unemployment rates, inflation levels, interest rates,
economic growth, taxation and average disposable income. Political and legal
landscaping concern laws, regulations, minimum levels of taxes or wages and
maximum levels of prices or quotas.
Internal environment focuses on
the resources the company has at hand as labor, finance, equipment, time and
other factors of production. It also analyses the marketing team concerning
structure, efficiency, effectiveness, correlation with internal functions and
other organizations. The internal marketing planning process, its accuracy and
actuality, the product portfolio, new products, pricing and distribution are
areas the marketing internal audit is concerned in. It also focuses on market
share, sales, profit margins, costs and effectiveness of marketing mix.
The marketing audit studies also the current marketing plan, focused on
objectives, strategies and the marketing mix used to achieve these goals. It
also evaluates budgeting, staffing, training, developing, experience and
learning. The current marketing plan concerns also the market share, financial
targets as profit and margins, cash flow, debt and other indicators that need
to be balanced.
There are several approaches that can be used, for example SWOT analysis
for the internal environment, as well as the external environment. Other
examples include PEST (political-economic-social-technological) and Five Forces
Analyses, which focus solely on the external environment. Using SWOT a company
lists its advantages and disadvantages, strengths and weaknesses compared to
its competitors or similar products providers. It also includes an analysis of
the external factors that could help or hinder company's chance of success, as
well as an evaluation of internal practices and operations [4].
The marketing
mix – the strategic combination
of product decisions with decisions regarding packaging, pricing, distribution,
credit, branding, service, complaint handling, and other marketing activities.
Its elements are
the basic, tactical components of a marketing plan. Also known as the Four P's, the marketing mix elements are price, place, product, and promotion [1].
As a conclusion, marketing is a complex area of business,
selling, market research, transportation, storage, and advertising. Marketing
means the movement of good and services from manufacturer to customer. The main
elements of marketing are marketing research, marketing
audit and marketing mix.
References:
1.
Bebykh V.V. Basis
of Economics and Finance: A manual for students of economic specialties of higher educational
establishments / Bebykh
V.V. –
Chernivtsi: BSFA, 2008. – 264
p.
2.
Cherenkov V.I./ Evolution of marketing theory and the transformation of
the dominant paradigm of marketing, Messenger St. Petersburg University (2004).
3.
Hall, Robert E., Taylor, John B. Macroeconomics: theory, performance,
and policy. – 4th ed. W.W. Norton and
Company, 2006. – 637 p.
4.
Hyman, David N. Modern microeconomics:
analysis and applications. – 2th ed. Irwin, 2009. – 689 p.