Pedagogical
Forms of student training based on informational technologies.
Shmakova A. P.
Dyakonova
O. O.
Abstract
This
article describes the forms of training based on informational technologies
that contribute to preparing students for professional careers (a multimedia
lecture, laboratory works based on informational technologies, distance
learning, defence of the creative projects on the basis of informational
technologies). Detailed schemes of interaction between teacher and his
students can effectively train a specialist meeting the requirements of the
modern informational society.
Key words
Informatization of
education, forms of training, students training, informational technologies,
distance learning, creativity.
I. Introduction
According to different
social, technical and technological changes in the modern educational system, there
appears the particular change in the traditional, classical forms and methods
of teaching. Nowadays they are enriched with new informational technologies. Every
present-day teacher has to meet the requirements of the modern informational
society and should be ready to train his students with the help of some new informational
technology means.
II. Problem statement
The present system of the future specialists training supposes that the most
effective forms of training are based on the didactic possibilities of the informational
technologies: multimedia lectures, laboratory works based on informational
technologies, written tests of self-control aimed at work the creation of particular
electronic materials, distance learning, the defense of different creative projects.
III. Results
Today one of the
most popular forms of teaching is a multimedia lecture, which involves the
active use of informational technologies in the demonstration mode. O. V. Yakovleva
said that in general this type of lecture can be named a computer presentation
[3. 47]. The way of presenting the information in a multimedia lecture, its
sound and graphics may vary depending on the goals and objectives, the specific
character of the whole training course, the age of the students and some other
features.
A multimedia lecture
is significantly different from the traditional lecture that we are used to
dealing with. Here the most important for us is the correlation of particular visual
images, written text and color schemes. Explaining the impact of the multimedia
effects on the knowledge digestion Richard E. Mayer makes reference to the
cognitive theory of knowledge. The main idea of the theory consists in the
availability of the two main channels of information perception: visual and
auditory. That is why while presenting the lecture one should tend to the
participation of both channels, but try not to overload them. In particular,
the duplication of the same information through the printed text and verbal
narration leads to the overload of both channels. Proceeding from the following,
two basic requirements for building a multimedia lecture can be formulated. The
first requirement is the following: the information should be presented in a brief
written or graphic form (a reference scheme or a model) with a detailed verbal
description. According to the second requirement it is reasonable to use some
additional effects like brightness, contrast, extraneous sounds.
Having studied the
role of the teacher and the potential of the informational technologies, we
construct a model of the interaction of a lecturer and his students during the
multimedia lectures (diagram 1.).
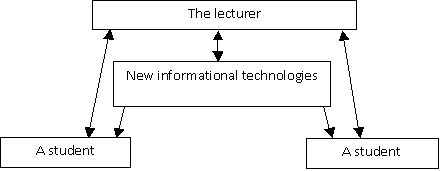
Diagram 1.
Multimedia lectures.
In the diagram 1 the
arrows indicate the direction of information flow, providing the informational
message. The lecturer takes an active role in the multimedia lecture. While
explaining the new material, he relies on the informational product, which he
controls himself. His students receive the relevant information both from the
teacher and from the screen of the projector. In turn, a multimedia lecture may
be organized as a problem lecture, a lecture of two people, a tutorial lecture,
a provocative lecture, a dialogue-lecture.
Laboratory works
involving the informational technologies are based on the training and
demonstration mode. They suggest a group or individual work with the help of
the methodological software that implements the opportunities of different multimedia
technologies and the Internet technologies. This form of teaching allows to
realize a differentiated approach to each student and to make their work much
more mobile and efficient.
During the laboratory
classes the students can work with different informational technologies having
the property of interactivity. It can be realized in learning a new material
with the help of an electronic textbook or completing a computer-based test,
etc. A student during such labs can put his individual speed and sequence of
operations according to his abilities and temperament.
This form of
training is different from all the other forms according to the fact that the
student takes an active role in the educational process. He can ask his teacher
different questions, communicate with the other participants in the group, interact
with the educational software (go to another slide of the presentation, view the
necessary page of his electronic textbook, change the data of the model of the
process or of the events etc.). It is shown in diagram 2.
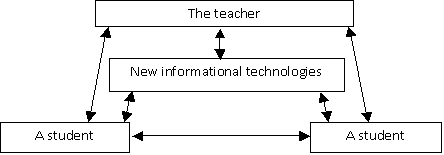
Diagram 2.
Laboratory works based on the informational technologies.
Because of the
transfer to bachelor's and master's degrees in Russia the organization of the educational
process is changing itself and there is a sharp increase in hours assigned for self-control
work. In this regard, there appear a lot of new problems and questions connected
with the organization of self-control work. These problems can be solved by
using the informational technologies in the educational process. That is why
the self-control work is a special form of organization of the learning process
[1]. Informational technologies can effectively increase the part of independence
in learning. Due to increasing independence we can notice the significant
increases in the creative component of the job.
The mode of distance learning is a variety of self-study lessons. They
became very popular with the development of the Internet. One of the most
common Internet technologies is the e-mail. Even the distance learning is based
on its opportunities. This method of learning is looked upon as "a new and
effective form of training with the use of personal computers, electronic books
and the Internet [2. 64] ".
If you use the e-mail
the main load in the speech aspect goes to the written speech, which makes it
impossible to use intonation, rhythm or timbre of a voice. The correspondence
involves a particular style of writing, which differs from the oral speech in longer
and more complicated sentences or the vocabulary. It is difficult to measure the
perception of the internal state of the student; his attitude to the activities,
the degree of his motivation because the written language may not reflect the
emotional state of the student. However, this form of learning solves a wide
range of aims. For example, those students who could not attend one or several
lessons for any reason can be provided with necessary electronic materials of
the multimedia lectures or some practical exercises for self-studies. Also using
the global Internet a teacher can ask his students a number of questions and
get answers. E-mails can be used for sending the completed work or assignments
and for exchanging the views, etc.
Distance learning
may be the main form of learning, and can be used as an auxiliary form of
training, supplementing the traditional ones. With this method of communication
the teacher and his trainee interact only through a global computer network,
without any direct contact (Diagram 3.).

Diagram 3. Distance
learning.
After the student defends
his design task for any discipline independently or as part of the creative
team, he can defend his project with the help of informational technologies,
such as presentations. The student makes a presentation of his creative project,
or produces an electronic model of the studied phenomenon. In the process of
defending his creative work the student demonstrates his own electronic
product, also showing his communicational and organizational abilities. The
process of defending of the creative projects based on the informational
technologies increases the communicational and verbal culture of the student.
During the process
of analysis and evaluation of the demonstration material the teacher and the other
participants interact with each other, but do not interact with an electronic
resource, they can only watch it. So the teacher and the group of students monitoring
and evaluating the task have only one-way communication with the informational
technologies (Diagram 4.).

Diagram 4. Defence
of the projects based on the informational technologies.
IV. Summary
Informational
technologies are the means of training a professional that meets the
requirements of the modern society [1]. These forms are aimed at involving
students in different creative learning activities based on informational
technologies.
Literature
1.
Soboleva, M.L. Informational
and communicational technologies in the system of training of future science
teachers / M.L. Soboleva / / The development of the national system of educational
informatization in health-educational environment: the scientific notes. No.
27. - M.: UIS RAS, 2008. - P. 107-110.
2.
Trainiov, V.A. Informational and communicational pedagogical technologies
(generalizations and recommendations): Textbook / V.A. Trainiov, I.V. Trainiov.
- 4th edition. - M.: Publishing and Trading Corporation "Dashkov &
Co», 2009. – 280 p. ISBN 5-94798-824-0.
3.
Yakovleva, O.V. Investigation of possible use of informational and
communicational technologies in shaping the communicative competence of
students of pedagogical universities: post graduate’s thesis in pedagogical
sciences: 13.00.08 / O. V. Yakovleva. - St. Petersburg, 2007, - 166 p. with
illustrations.