Ýêîíîìè÷åñêèå íàóêè/ 16.Ìàêðîýêîíîìèêà
Junussova M.G., postgraduate student of 1 course
Salzhanova Z.A., doctor of economics, professor
Karaganda Economic University, Kazakhstan
ANALYSIS OF THE STRUCTURE OF GDP AND THE CURRENT STATE
OF THE INDUSTRY KAZAKHSTAN
One of the main
macroeconomic indicators estimating results of economic activity is the Gross
Domestic Product (GPI). It characterizes not only a modern level of development
of national economy of the country, but also feature of its branch and
territorial structure, efficiency of functioning of its certain spheres,
branches and regions, degree of an involvement into world integration
processes, etc.
In economy of
Kazakhstan stable growth rates of GDP are observed. According to the Agency of
the Republic of Kazakhstan on Statistics, average GDP growth of the republic
for years 2009-2013 amounted to 5.2%. GDP volume in 2013 made 35275 billion
tenge that is 6% above than a level of 2012.
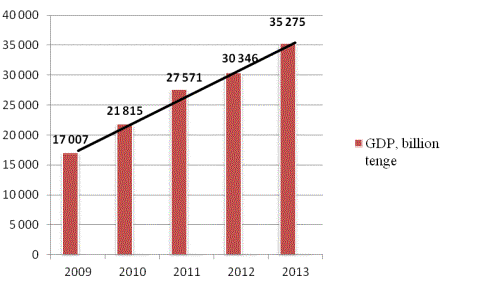
Figure 1. Dynamics of GDP of Kazakhstan for 2009-2013.
The lowest GDP
growth rate was 1.2% in the crisis year of 2009. In the period 2010-2011.
experienced significant growth in GDP on average 7.4% per year.
Following the
results of 2013 is observed moderate growth compared with previous years.
According to Agency of statistics of RK growth rate of GDP in real terms made
6% whereas in 2012 GDP grew by 5%. However, the growth indicators of
Kazakhstan's economy has not yet reached pre-crisis levels, which in 2006-2007.
GDP growth was 10.8%, but already there are signs of a gradual economic
recovery. According to the results of Kazakhstan's GDP in 2013 was 35 275
billion tenge, which is 10.5% more than
in 2012, while inflation for the year was 4.8%. GDP volume per capita for 2013
made 2 070 thousand tenge or 13 612 US dollars that is 12,3 % higher than an
indicator for previous year.
GDP growth in 2013 compared with the previous year was
achieved by increasing the dynamics of growth in sphere of manufacture of
goods.
In the dynamics
compared to the previous year Index of physical volume goods production sector
increased from 99.5% to 103.3%, while the services sector has slowed growth
from 110.4% to 107.4% due to the decrease in the rate of growth of the physical
volume in all business areas (retail, communications, financial services,
transport, etc.). The largest share in the GDP accounts for the manufacturing
sector services - 52.6%, and the
production of goods - 40%, and taxes on products and imports - 7.4%. [1]
Despite the high
economic growth rates observed over from 2009 to 2013, the structure of GDP by
industry did not change significantly.
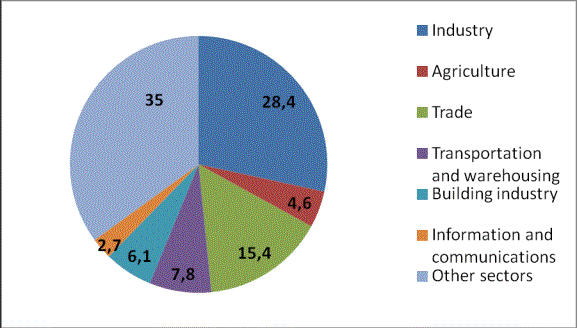
Figure 2.
Structure of GDP of Kazakhstan on sectors in 2013
The share of
industry in GDP occupies 28.4%. Industry is the leading sector of the economy
of Kazakhstan. A feature of industry of Kazakhstan is its exceptional provision
of own rich mineral resources. A high level of availability of natural
resources allows to develop complex diversified structure of industry, which is
based on sectors of mining industry, such as extraction of fuel and energy
minerals, mining of iron ore and non-ferrous metals, manufacturing sectors, the
leading ones are: metallurgical industry and manufacture finished metal
products, metal and mechanical
engineering, production of chemical,
petrochemical and pharmaceutical products, food processing, production of
textile and leather products and others.
In 2013, volume
of industrial production in monetary terms amounted to 17,834 billion
tenge. On an indicator the volume index
for the industry in 2013 is observed an increase of 102.5% after slowing down
in 2012 to 100.7% as a result of increasing volumes in the mining sector due to
the increase in monetary terms of production of oil and metal ores.
The analysis of
structure of the industry of the country indicates the predominance of the raw
materials sector. So, for the period from 2009 to 2012 in a total industrial
production on the share of manufacturing accounted for just over 30%, mining
industry - more than 60%.
Let us analyze
results of the work of major industries, such as mining and manufacturing.
Mining and
smelting industry - is one of the most competitive and dynamically developing
sectors of industry of Kazakhstan. It employs nearly 164.5 thousand main
professions. In Kazakhstan, concentrated 30% of world reserves of chromium ore,
25% - of manganese ore, 10% - of iron ore. Reserves of copper, lead and zinc
are respectively 10% and 13% of the world. The total geological reserves and
the predicted coal resources of Kazakhstan are estimated at 150 billion tons.
Of the 105 elements Mendeleev`s table in a subsoil of Kazakhstan holds 99, 70
explored elements, involved in the production of more than 60 elements.
Mining and
metallurgical industry in Kazakhstan in the last years is one of the most
dynamic sectors of the domestic industry. As of the end of 2013 the volume of
the mining industry made 10 697 billion tenge, having increased in comparison
with an indicator of 2012 by 4,4%. At the same time the volume index was
103.3%whereas in 2012 the volume index was 100.4%. Despite the growing
indicators the mining sector, the industry has not yet recovered to pre-crisis
levels (107.2% in 2009-2010.), mainly due to the deceleration
in growth in the sector of oil and gas extraction.
Table 1
Index of physical volume of production by economic
activities
|
Type
of economic activity |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
|
Mining
and quarry development |
107,2 |
107,2 |
101,3 |
100,4 |
103,3 |
|
Mining of coal and lignite |
104,4 |
106 |
101,8 |
100 |
|
|
Crude oil production |
108,2 |
105,8 |
100,5 |
98,9 |
103,2 |
|
Extraction of natural gas |
105,5 |
106,2 |
105,8 |
106,3 |
103,7 |
|
Mining of iron ore |
100,1 |
113,4 |
101,7 |
100,8 |
98,7 |
|
Mining of non-ferrous metals |
107,3 |
105,7 |
99,9 |
106,1 |
108,8 |
The oil and gas
industry of the republic is the diversified and export-oriented, considerably
predetermining development republic economies. The government of Kazakhstan
plans to enter in 2015 the first ten oil-producing countries of the world and
as appropriate to increase the export potential. However implementation of
these plans can prevent objective difficulties in development of the majority
of large-scale deposits of Kazakhstan - production conditions on them are
considered difficult, hydrocarbons on the chemical composition also belong to
category "problem" that considerably increases cost of oil production
and the requirement to ecological safety.
For reasons of
great technical complexity and significant environmental risks not started oil
extraction from the giant deposit "Kashagan" in the Caspian Sea.
Taking into account oil extraction on Kashagan, it is planned to increase oil
extraction to 130 million tons. Now Kazakhstan exports 8,5 of each 10 tons of
the extracted oil.
For the economy
of Kazakhstan possessing considerable capacities for production, the coal
industry is the oldest and traditionally occupies a considerable share in the
fuel and energy balance (FEB) of the republic. This is due to the widespread
use of cheap Ekibastuz coal open-pit mining, which in many ways contributed to
the low cost of electricity, which is important for the competitiveness of the
national economy. To date, the coal share in FEB of Kazakhstan makes about 63%,
a share of natural gas of 12%, oil of 20%. Renewable sources account less than
5% and are presented practically only by hydraulic
power industry. Coal respectively is the main fuel of the Kazakhstan electric-power
industry, about 70% of the general generating power.
Hydroelectric power stations account for about 11%, gas turbine and steam
turbine power plants with natural gas and fuel oil for about 20% of the total
generating capacity.
On production
volumes Kazakhstan is included into ten the largest countries of producers of
coal in the world, and among the CIS countries takes 2nd place after Russia.
Kazakhstan
strengthens the positions on production and export of coal that promoted by the
outlined tendency of growth of its consumption in the world, first of all, in
electricity generation that is connected with the accelerated development of
the largest Asian economies of India, China, and also high volatility at the
markets of hydrocarbons of oil and gas.
It should be
noted that at the present time almost all types of energy there is a
significant excess of the amount of their production of intra-consumption,
which suggests considerable domestic potential, as well as large export potential
of Kazakhstan's energetics. [2]
At present time in Kazakhstan there is a topical issue
about the development and support of manufacturing enterprises. By the
manufacturing industry relate machine-building enterprises, enterprises of
ferrous and nonferrous metals, rolled products, chemical and petrochemical
products, machinery and equipment, wood products and pulp and paper industry,
cement and other building materials, products of light and food industry, local
industry. In the manufacturing industry
since 2010 has been a tendency of advanced growth in comparison with mining
industry. In 2012 in comparison with 2011, the growth in the manufacturing
sector - 101.2%, in the mining industry - 100.4%, in the industry in general -
100.7%. But in 2013 in comparison with 2012 growth rate in the mining industry
(103,3%) is more, than in manufacturing
industry (101.9%). Specific weight of manufacturing industry in 2013 in
structure of GDP decreased from 11.3% in 2010 to 10.9%.
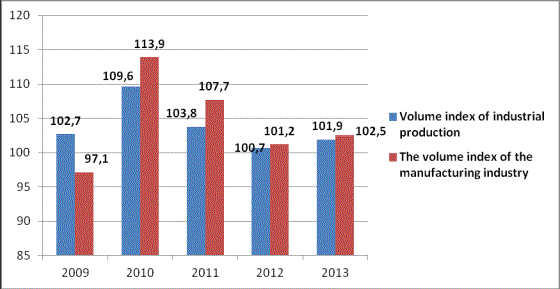
Figure 4. Volume
indices of the manufacturing industry
In the
manufacturing industry in 2013 in comparison with 2012 production growth
observed in mechanical engineering (114.4%), chemical industry (103.6%),
manufacture of coke and refined petroleum products (101.5%) and pharmaceutical
industry (101 , 3%).
The decrease was
in light industry (99.2%) and metallurgy
industry (95.2%).
Ferrous and
nonferrous metallurgy important branches of the industry of Kazakhstan. The
share of metallurgical industry and manufacture finished metal products account
for about 10% of all industrial output.
Ferrous
metallurgy is one of the most basic sectors of industry in Kazakhstan,
providing not only internal consumption, but also forming a profitable export
item of the country.
In 2013,
Kazakhstan reduced of crude steel smelting, compared with 2012 by 7.9% to 3.477
million tenge. During the year the production of flat products in Kazakhstan
has dropped by 5.2% to 2.277 million tenge, tin plate and tinned sheet metal -
by 46.6% to 85.8 thousand tenge, while galvanized rolled steel increased by
10.7% to 513 7 thousand tenge. In addition, the production of ferroalloys
decreased by 1% to 1.708 million tenge.
Decreased
production of metal products caused by the reduction demand for metals in
importing countries China and Russia. As a result - cheapening of metals by 10
- 20%, and a small reduction in production.
The mechanical
Engineering is a leading industry, providing machines, devices all sectors of
the economy, playing an important role in the intensification of production, in
increasing labor productivity, accelerating economic and social development of
the country in general and the its regions.
The mechanical
engineering share in the total amount of industrial production increases in
dynamics since 2009. Specific weight of sector in a total amount of industrial
production of the republic in 2013 made 4,8%, in manufacturing industry
of-14,7%.
If in 2008 the
mechanical engineering of Kazakhstan was presented by 3 main subsectors, in
2012 the mechanical engineering has already presented by 6 main segments:
manufacture of motor vehicles; repair and installation of machinery and
equipment; Manufacture of electrical equipment; production of electronic and
optical products, and others.
In the structure
of the industry is still dominated by the repair and installation of machinery
and equipment - 40% of total output. Production of vehicles, including
automobiles, in the aggregate occupies 35% of total output.
Growth in the industry
occurred due to increase in production vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers. A
significant increase in production observed in the production of passenger cars
by 5.9 times over the period 2009-2013.
In 2013, were
produced 37,469 units of passenger cars, which is 2 times more than the same
period of last year. In four years in branch more than 1 billion euros
investments were attracted. Investments, first of all, in the form of
technologies of global manufacturers of machine-building production: GE, Alstom,
Toyota, Siemens.
During
implementation of the state program in sector thousands of new high-performance
workplaces are created. The special impulse received the automotive industry,
production of railway equipment, agricultural engineering.
There was the
whole innovative cluster of railway mechanical engineering: locomotives, power
packs, wagons, and spare parts. All this was possible also because
manufacturers of wagons have received loans and leases of state development
institutions amounting to more than 10 billion tenge.[3]
The chemical
industry is an important and high-perspective sector of the national economy.
The structure of the Kazakhstan chemical industry consists of the production of
basic chemicals, fertilizers and nitrogen compounds, plastics and synthetic
rubber in primary forms, lacquers and paints, cleaning products, detergents,
pesticides and other agrochemical industries.
About 26% of all
chemical products are consumed by own industry, and the rest goes to the needs
of other sectors of the economy: the electronics industry, the production of
accumulators, energy-efficient construction materials, mechanical engineering,
light industry, etc.
The share of
chemical branch in GDP grew from 0,32% in 2009 to 0,53% in 2013. Despite it,
this indicator is lower than an indicator of the countries with the developed
chemical industry which averages 5%.
From 2009 to 2012
the volume of export of production of chemical industry of advanced processing
in nominal terms increased by 67,7%. The gross value added in sector increased
by 3 times.
In 2009, this
indicator was equal 45.96 billion tenge, and already in 2012 - 141.8 billion
tenge. Labour productivity in the chemical industry increased by 3.7 times, in
2009 - 13 thousand dollars per man, and in 2012 - 48,300 dollars. The volume of
production of chemical industry from 2009 to 2013 increased by 69.5% and
amounted to 179.9 billion tenge. The increase in output of chemical production
is connected first of all with modernization of the old enterprises.
In the chemical
industry of Kazakhstan has recently passed the modernization of existing
enterprises, opened new production, was created the institutional framework of
the sector. The main directions of modernization of existing enterprises: increasing
productivity and resource efficiency, diversification and increase in volumes
of production.In the process of modernization involves three major companies:
LLP "Kazphosphate" LLP "KazAzot" and JSC
"Kaustik".
Modernization LLP
"Kazphosphate" will develop the production of sodium
hexametaphosphate. Also, the company will release 4 more new products as far as
of modernization till 2020. After modernization number of personnel will
increase by 270 employees - up to 6100 people, labor productivity increased
more than 4 times, the energy intensity of production will decrease by 30%.
Modernization on
the LP "KazAzot" allowed to increase labor productivity by 1.5 times.
The volume of output, in turn, grew by 50%. In JSC "Caustic" has been
restored thanks to the of modernization production of caustic soda, chlorine
and its products on the basis of modern membrane technology.
To date, foreign
investors are reluctant to invest their funds in the chemical industry.
However, with the launch of major projects in 2020 may increase foreign direct
investment in the production of agricultural chemistry (LLP "«Evrohim Udobreniya»», Kazakhstan
Potash Corporation), polymer products (LG Chem) and engine oil ("Lukoil»,
Hill Corporation). The structure of the economy of Kazakhstan to date, despite
a number of adopted and implemented by government programs is focused on mining
industries, which determines its high dependence on an environment of the worldwide markets. [4]
Reducing this
dependence and accordingly increase the stability of the Kazakh economy during
the global crisis, accompanied by a decrease prices in commodity markets, and
is a priority problem of modernization and diversification of the economy in
general and industry in particular. Diversification of the economy is the
appearance of new growth points, which at the same time can become supports
neutralizing the negative global crises.
The first stage
of the modernization of industry initiated by the Government since the
implementation of the State Program of Forced Industrial-Innovative Development
of Kazakhstan for the period 2010-2014. The implementation of the first Five
SPAIID and programs implemented within its framework, gave impetus to start the
restructuring of the national economy.
Main positive
results of SPFIID:
1) laid the foundations of a modern industrial policy in the Republic of
Kazakhstan. Adopted the basic normative legal acts, tested various tools
support industrial development and new policy directions. In particular,
mechanisms were launched to attract FDI and export support, started the process
of transformation of special economic zones.
2) started diversification of the economy by accelerating the development
of manufacturing industry, increasing the non-oil exports and attracting FDI in
the non-primary sector.
3) received support major new industrial projects implemented in the
framework of the Industrialization Map and avoided reduction of production.
4) the number of employed in
industry (for 4 years) increased by 9.3% and exceeded 1 million people (1004.4
thousand people). Within the framework of the Industrialization Map created
more than 60,000 new jobs in the manufacturing industry, allowed to avoid rise
in unemployment.
Through
the implementation of the SPFIID 2010-2014 has achieved significant progress in
the development of industry in Kazakhstan.
The
SPFIID new program, designed for 2015-2019 years, is a logical continuation of
the first "Five-Year Plan" and takes into account the experience of
its implementation.But the main difference is that the second stage will be
more focused on the development of the manufacturing industry is with the
corresponding concentration of efforts and resources on a small number of
priority sectors, regional specialization using the cluster approach, and
effective regulation of the industry.
To provide the
real modernization of the Kazakhstan industry directed on creation of
productions, competitive at world level, it is required to decide on priorities
of sector development. [5]
Sectors,
considered the most perspective and priority in developed countries, should be
given consideration in Kazakhstan in the process of modernization of the
national economy. Experience of world crisis showed that economies with high
export orientation appeared the most vulnerable. Consequently to improve the
stability of the national economy and reduce its dependence on external factors
need to develop new industries in Kazakhstan, focused primarily on domestic
demand, often more stable in comparison with an external, which also may be
regulated at the national level in case of crisis.
References:
1) Statistical
Yearbook "Kazakhstan in 2013."
2)
PricewaterhouseCoopers. Metallurgical industry and Mining in Russia and the
CIS. Mining and metallurgical industry in Kazakhstan, 3 edition, Astana, 2012
3)
"Kazakhstan Industry Development Institute". Digest - mechanical
engineering, Astana, 2014
4)
"Kazakhstan Industry Development Institute". Digest - chemical
industry, Astana, 2014
5) The concept of
industrial-innovative development of Kazakhstan for 2015-2019