Ñîâðåìåííûå èíôîðìàöèîííûå òåõíîëîãèè/ 3. Ïðîãðàììíîå
îáåñïå÷åíèå
Candidates of technical
sciences: I.V. Dolotovskij, E.A Larin, N.V. Dolotovskaya, graduate student A.V.
Lenkova
Saratov State Technical University, Russia
Information
and communication technology in human resource support energy audits and energy
efficiency of industrial enterprises
An energy audit (EA) of
industrial enterprises is conducted in order to improve the efficiency of fuel
and energy resources (FER) by upgrading the equipment, optimizing of operating conditions,
introducing modern technologies for
creation of high-energy technology
(technological) systems. This goal is achieved in several stages by using
information and communication technologies. One of the most important stages of
the EA enterprises is the analysis of actual consumption and the generation of
(FER), the state of their long-term planning and regulation. It is crucial especial for enterprises which have complex
technological structure of the main and auxiliary facilities, where the energy
supply is provided by external and internal production systems with multi-level
relationships with technology installations.
Training of energy audit
experts plays the pivotal role in solution of problems at this stage. The
experts have to be aware of principles of system analysis of complex
technological and power equipment at industrial enterprises which have various
manufactured products. The information-analytical system is realized and used
for training of such specialists. This system consists of the main database
with the appropriate control systems: normative and methodical documents;
methods of calculating the energy efficiency of equipment and installations;
programs and instruments for measurements; standard consumption indicators and generation of energy; projects improving
energy efficiency of devices and equipment; technical information on modern
equipment (Fig. 1).
The IAS’s realization is
performed at all levels of the company’s hierarchy (equipment, installation, manufacturing, power
supply subsystem, the enterprise as a whole). It is necessary for the solution
of the following complex of interrelated problems: identification of all FER
types and water flows; the organization of the planned, actual and normalized
balances by type of used / generated of FER; the evaluation of an energy efficiency and analysis of the deviation of the
actual and specific rate from the regulatory consumption / generating FER and
water consumption for each installation, and production company.


Fig. 1. Block diagram of the IAS
The fundamental organization
of the IAS main fourth unit is based on the block-hierarchical principle and
realized in individual interconnected components - program modules (PM), which
are discrete elements, admitting the separate compilation, integration with
other elements and downloading.
The basis of each MP is the
software (SW), it is developed using the «Stepwise Refinement». On the first stage the data and methods
of their analysis were identified for the energy sector of the company in the
whole, on the second-stage the determination’s procedure was carried out in an
ever-increasing level of detail (manufacturing, installation, equipment).
Method of «Encapsulation» was used in the development of the software calculating the energy
performance at the level of plant and equipments. External interfaces of
modules only were left visible for users. This interfaces exactly define all
the valid operations on them (data entry, calculation, display the results, the
transfer of information) with a hidden software implementation of the module.
The calculations with using developing PM are carried out in automatic mode (no
user interaction) and mechanized mode (with user’s interaction) after entering
the initial data. In the latter case, appropriate options for communicating
with program components of the module are provided in the user interface.
The relationship between the
PM of the fourth main IAS’s unit is performed by communication channel, which
is activated by users (Fig. 2). A conclusion of the PM contains calculation of
calculating (automatically updated) information for each type of FER:
![]() - data on the
equipment of the plant’s installs with
different structures for each type of FER and the updating by communication
channel I;
- data on the
equipment of the plant’s installs with
different structures for each type of FER and the updating by communication
channel I;
![]() - the total individual hours of use/ generation of FER by equipment of
installation N enterprise M for each type of resource;
- the total individual hours of use/ generation of FER by equipment of
installation N enterprise M for each type of resource;
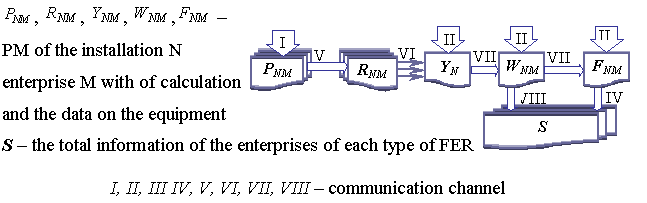

Fig. 2. The diagram shows interrelation of
the IAS PM
![]() - consumption /
generation of the FER and water consumption in accordance with the operation’s
mode of the installation’s equipment
during fixed period of time. This information is represented in the form of
five interrelated automatically updated information blocks; correction of rates
of loading facilities can be done by the
additional information channel II;
- consumption /
generation of the FER and water consumption in accordance with the operation’s
mode of the installation’s equipment
during fixed period of time. This information is represented in the form of
five interrelated automatically updated information blocks; correction of rates
of loading facilities can be done by the
additional information channel II;
![]() - automatically formed indexes of consumption / generation of the FER and water
consumption during calculating period of operation (month, quarter, year)
are updated by the communication
channel VII; in addition to identification of the specific rates of the
consumption / generation of the FER and water consumption, users can make
adjustments to expenditures of planned technological flows by communication
channel II;
- automatically formed indexes of consumption / generation of the FER and water
consumption during calculating period of operation (month, quarter, year)
are updated by the communication
channel VII; in addition to identification of the specific rates of the
consumption / generation of the FER and water consumption, users can make
adjustments to expenditures of planned technological flows by communication
channel II;
![]() - formed on the
production’s installations in accordance
with values of measuring devices, the actual performance of the absolute and
specific rates of the consumption / generation of the FER and water consumption
during calculating period of operation; after the activation of channel III
information about consumption of technological flows are updated.
- formed on the
production’s installations in accordance
with values of measuring devices, the actual performance of the absolute and
specific rates of the consumption / generation of the FER and water consumption
during calculating period of operation; after the activation of channel III
information about consumption of technological flows are updated.
Final results are presented in the form of
automatically constructed diagrams of the dynamics of the planned and actual
consumption / generation of the FER and water consumption on the background of
the dynamics of production or consumption of the technological flows and the
ability to compare actual data with the regulatory values (Fig. 3).
![]()


Fig. 3. Detail of the results
of the PM with the dynamics of the specific electricity consumption by
equipment of sulfur’s manufacture.
Designed IAS enables training and development of
professionals, which perform an energy audit of industrial enterprises.
It is necessary to note that the II, III communication channels can act
as exits of other information systems of the company - process control and
manufacturing automation systems. It allows to use the IAS for creation of elements of corporate
information systems of the surveyed companies and design of own computerized
systems for working out of technical decisions for increase of object's power
efficiency with need to pay attention on modern trends of the technological
processes and equipment, change economic, climatic, environmental, and other
influencing factors.
Literature
1.
1. A system
of automated accounting and planning at the enterprise: a stalemate. Number 63
537 RF / EA Larin, NV Dolotovskaya, I. Dolotovsky. - ¹ 2007106539/22 (007086),
appl. 20.02.07, publ. 27.05.07.
2.
2. System,
"Energy supply": a computer program number 2010615353 / EA Larin, IV
Dolotovsky, NV Dolotovskaya. - ¹ 2010613798; appl. 29/06/10; reg.. 20.08.10.
3.
3. Larin 3
EA Dolotovsky IV, NV Dolotovskaya Energy complex gas processing plants. Systems
analysis, modeling, valuation. - Moscow: Energoatomizdat,2008.-440C.
The work was supported by the Russian Ministry of Education (CC 14.
740.11.0107)