Ryzhkova
Julia Anatolevna, Sergeeva Elena Sergeevna,
PenzGU, Penza
Analyze the dynamics of rouble to dollar rate in the
years 1993-2012
Fluctuations
of the rate of exchange influence the interrelation of export and import
prices, the competitiveness of firms, the profit of the enterprises. Sharp
fluctuations of the rate of exchange strengthen instability of international
economic, monetary and financial relations in particular, cause negative
socio-economic consequences, the loss of the ones and the winnings of other
countries.
The
problem of fluctuations of the rate of exchange is very topical for Russia, as
the part of Russia in the world economy in 2010 was about 3.7%. More than half
of GDP is generated through exports[1].
Let's
analyze the dynamics of rouble to dollar rate in the years 1993-2012, the state
at the end of the month particularly [2].
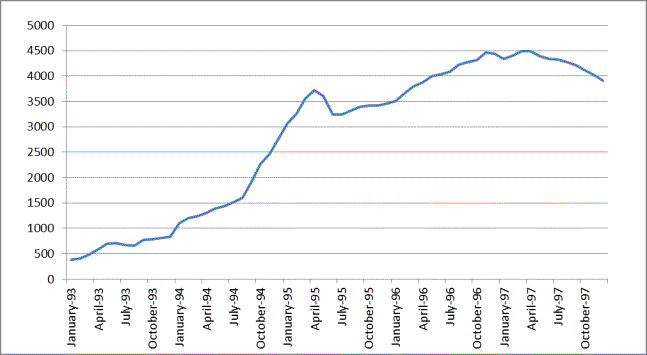
Pic 1. Dynamics of rouble to dollar rate for 1993-1997
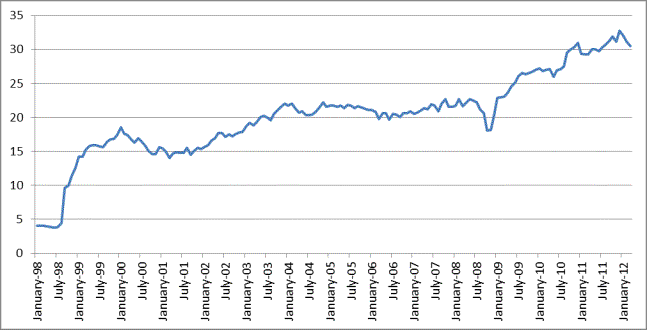
Pic 2. Dynamics of rouble to dollar rate for 1998-2012
Let's
analyze the first decade (pic 1). It is characterized by a crisis state of the
Russian economy, in which the rate of exchange of the ruble decreased steadily,
stimulating the rising of inflation.
The
currency crisis in the autumn 1994, the culmination of which was the
"black Tuesday" of 11 October 1994 (in a day rate of us dollar
increased from 2833 to 3926 rubles for a dollar), was a sign to a sharp change
of the macroeconomic policy in Russia. The main task was to decrease the
inflation at all costs. In the foreign exchange field the decision provoked the
introduction of the exchange rate band regime in 6 July 1995 - official limits
of fluctuations of ruble to dollar rate.
Fixed limits were supported by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation with
the help of interventions on the stock exchange and the interbank foreign
exchange markets [3].
On January
1, 1998, the denomination of ruble took
place, in ratio of 1000 to 1.
In the
conditions of the currency crisis of August 17, 1998, the ruble to dollar rate fell
in half a year period for more than 3 times - from 6 rubles for dollar before
the default up to 21 rubles for dollar in January 1, 1999. The government had
to lower and significantly widen the currency corridor - up to 6 - 9, 5 rubles.
However, there was a sharp fall of ruble (in three weeks it he fell for 3,3
times in comparison with the level of the 17th of August). In fact the currency
corridor stopped its activity, and the rate of exchange of ruble became
floating again.
the was
an increasing of rouble to dollar rate in the years 2000-2003, reaching a level
of 31,88 rubles to a dollar. From 2003 till 2008 the dollar rate varies from 19
to 22 rubles for a dollar. On the 16th of July 2008 there was a maximum drop of
the ruble to dollar rate with regard to the denominated rouble of 1998: 23,148 rubles for a dollar. But in half a
year was noted the maximum rate of dollar
(36,43 rubles for a dollar). After that it decreased and continued to change with
some ups and downs, and for today the price is 30,53 rubles for a dollar.
Decrease
or an increase in the rate of exchange has both positive and negative sides. In
particular, by decreasing in the exchange rate of the national currency( if
there's no opposition from other factors) exporters either receive export award
while exchanging of foreign currency, which has risen in price in the national
currency, which, by-turn has fallen , or have the ability to sell goods at
prices below the world average. But at the same time decrease of the rate of
exchange of the national currency affects the rise in imports, which stimulates
the growth of prices in the country, the decrease in import of goods and
consumption, or the development of the national production of goods instead of
imported ones. The exchange rate reduces the real debt in the national currency
and increases the burden of the external debt denominated in foreign currency.
Unprofitable becomes the export of profits, percents, dividends, which receive
foreign investors in the currency of the host country. These profits are used for
buying goods for domestic prices and their subsequent export.
By
increasing the exchange rate of the national currency the domestic prices
become less competitive, the effectiveness of export falls that can lead to
stagnation of export-oriented industries of the national production. Imports,
on the contrary, increases. Stimulated by the inflow into the country of
foreign and national capital, increases export of profits on foreign
investment. Decreases the actual sum of the external debt denominated in foreign
currency.
As
Russia is a major exporter of resources, on the one hand it is more profitable
to reduce the rate of the national currency, on the other - the strengthening
of the ruble exchange rate will also contribute to the improvement of the economic
situation, encouraging the banking sphere, in particular: stimulates the banks
to borrow abroad, leads to the active inflow of funds of the population. In any
case, the process of falling or strengthening of rouble exchange rate should be
controlled by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, the plan of economic
development of the country should be developed depending on the situation.
List of references:
1.
Выступление Министра
Э.С. Набиуллиной на совместном заседании коллегий Минэкономразвития России и
Минфина России, г. Москва, 25 апреля 2011г. // URL: http://www.economy.gov.ru/minec/press/news/doc20110426_06?presentationtemplate=docHTMLTemplate1&presentationtemplateid=2dd7bc8044687de796f0f7af753c8a7e&WCM_Page.ResetAll=TRUE&CACHE=NONE&CONTENTCACHE=NONE&CONNECTORCACHE=NONE
2.
ЦБ РФ, база данных по
курсам валют // URL: http://www.cbr.ru/currency_base/monthly.aspx
3.
Международные
валютно-кредитные и финансовые отношения: учебник / Под ред. Красновой Л.Н. –
М.: Изд-во «Финансы и статистика», 2005, 3-е изд., - 576 с.