Senior lecturer
Kuznetsova Y.A.
Karaganda State Technical University, Kazakhstan
Associate professor
Yassinskiy V.B.
Karaganda State Technical University, Kazakhstan
Network
technology of remote training at teaching the course of physics in technical universities
In 1999 in Law of Kazakhstan's
Republic “About education” [1] remote education in Kazakhstan has been defined
as a new, special mode of study. In this document remote educational technologies
have been defined as the technologies of training, which are carried out with
application of information and telecommunication means existing on distance.
Certainly, new mode of study has interested leading high schools of Kazakhstan,
and gradually began to take root first as experiment, including at the Karaganda
State Technical University since 2002.
Realization of remote
educational technologies [2] is carried out by following kinds: TV-technology,
network technology and a case-technology. The network technology provides
support with study-methodical materials; interactive interaction trained with
the teacher and with each other, and also administration of educational process
on the basis of use the Internet.
On physics department at our
university [3], the system for remote education MOODLE — “Modular Object-Oriented
Dynamic Learning Environment” [4] has been introduced.
The environment gives a
modular principle of training. The teacher all training course realizes in the
MOODLE environment — its sections, themes, etc., including and the supervising
block. All lecture, practical material and supervising tasks settle down in
MOODLE system to which the teacher has possibility to address in the course in
all teaching of a course. Apparently from Figure 1, in the created courses the
student has possibility to receive all material necessary for training, and
also performance of control and laboratory works [3]. In this system courses on
disciplines “Physics 1” and “Physics 2” and "Physics" for students of
all specialities under the confirmed working curriculums according to typical
curriculums are created.
The structure of electronic study-methodical
complex is presented in the form of following modules:
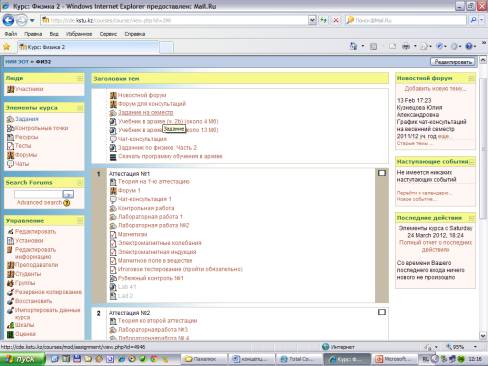

Figure 1. The “Physic 2” structure
1. The informational
module.
The informational module
includes:
The academic calendar, in
which the purposes and subject matter problems are described, by all kinds of
works, the list of the basic and additional literature, and also acquaintance
with point-rating system of marks and admission conditions for examination
2. The communication
module.
The basic component at
realisation of remote education by network technology is interactive dialogue
between teacher and student. For this purpose provided: the chats-consultations
which are passing with a necessary regularity, dialogue by means of various
forums, message exchange etc.
3. The Study-methodical
module.
This module includes:
Theoretical materials. These materials are
presented in various forms:
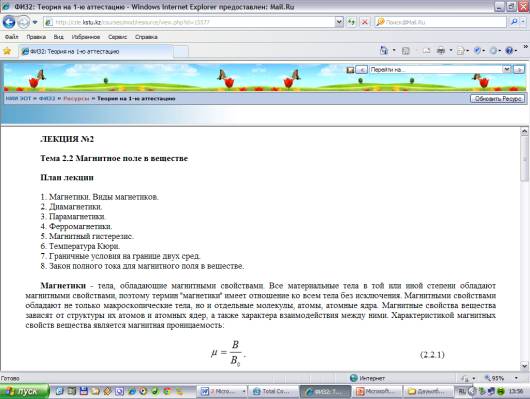
The unique electronic textbooks presented in HTML (CHM)
formats. Textbooks have: theoretical section, virtual laboratory, section for
performance practical tasks, help files, other information (fig. 2).

Figure 2. The electronic book “Physic 1”
The theoretical
section in the textbook is stated as much as possible in detail and supplied by
a considerable quantity of author's illustrations and animations. Such volume
of the information allows studying basic and additional course volumes.
The textbook also
has convenient system of the navigation, allowing to move to any section of the
textbook and to come back.
Shown textbooks possess
huge popularity as among students of internal and correspondence branches, and
among teachers
Besides, there is also more
short, so-called an Internet the version with which students can familiarise in
online a mode (fig. 3).
Figure
3. Online lectures
As it is known, as information
mastering happen:
People perceiving the most
parts of the information by visually.
People who basically
receives the information through the acoustical channel.
People perceiving the most
part of the information through other senses (sense of smell, touch, etc.) and
by means of movements.
People at which the
perception of the information happens basically through logic, by means of
figures, signs, logic arguments. This category, perhaps, not most numerous in
general among people. To schoolboys younger and middle classes such way of
perception of the information usually not famous.
by sight — 35%;
by acoustical channel — 5%;
by senses — 35%;
by logic — 25%.
For two last categories of
pupils in the given module began to join a new kind — video lectures (fig. 4), executed by
teachers of our department. This kind of teaching allows acquiring the
information in more convenient form.
. 
Figure 4. Video lectures
Materials for performance a practical training (fig. 5) include:
examination variants, examples of its performance, a file with the physical
constants, necessary formulas, an inquiry file.

Figure 5. Materials for
practical trainings
The virtual physical laboratory includes many
laboratory works. Each of works has: the virtual laboratory stand, theoretical
section, an order of performance of work.
The block from test tasks for
self-examination of student's knowledge. Here the student can estimate
the knowledge and quantitatively (quantity of the typed points) and qualitative
(what sections the student knows worse and what — is better). Similar “the test training apparatus” allows to generalise the
knowledge received at studing course and to be prepared to as for the total
testing going already “in offset”, and to the further control actions.
Student supposed to intermediate
certification for discipline after performance and delivery of all control
actions established by the curriculum.
In the offered system
following principles are most brightly expressed:
— A principle of training's presentation.
Students can see all studied material at once. To make teaching material more
evident do things that easily compatible with given environment: electronic
textbooks, presentations, audio- and videofiles etc.
— The system and sequence principle realized in
representation of a training course by a set of modules. In the beginning of
any employment, and also during nonlearning time, there is a possibility to
repeat the passed material, having come on the corresponding module of a course
in system MOODLE. The given system also assumes possibility of generalization
and material ordering.
Advantages of this educational
environment:
— The friendly
interface, work with system does not demand special knowledge;
— Flexibility in
creation of courses in system (ample opportunities of the teacher at course
creation, a choice of methods, modes of study and the control);
— Automation of the
course's content;
— High degree of presentation;
— Possibility of
student's self-checking. The student can pass the test, which will not be estimated,
and student will see the committed errors; besides, it is possible to organize
the fixed number of passage the test and number of attempts the answer on
question;
— Possibility to be
trained during any time convenient for the student;
— Possibility of repeated passage (studying) of a
material; always it is possible to return to the passed module.
Introduction of training
courses in system MOODLE has allowed to lift level of remote training
essentially. The created courses successfully work many years, but also in this
direction “there are no limits to perfection”. So, for example, in 2012 in
Republic Kazakhstan governmental order from 2012/01/19 publishes new “Rules of
the educational process’s organization on remote educational technologies” [2]
where is supplemented and changes principles of realization remote training.
Therefore courses are regularly supplemented with electronic training means;
the training technique is improved also.
The literature:
1.
Republic Kazakhstan’s law “About education” ¹319-III —
http://fdo.rii.kz/board/Zakon_ob_obrazovanii.pdf.
2.
The governmental order of Republic Kazakhstan from January 19th, 2012 ¹
112 “About the statement of Rules of the educational process organization on
remote educational technologies”— http://www.zakon.kz/pravovye-novosti/4474122-utverzhdeny-pravila-organizacii.html.
3. Organization’s
rules of educational process with application of remote educational technologies
in KSTU. Karaganda — 2010.
4. http://moodle.org.