Karachun V.V., Trivailo M.S., Mel’niñk V. N.
National Technical University
of Ukraine «KPI»
THE intensification of transference of culture broth
The
utility model refers to microbiology and may be used for cultivation of
microorganisms in liquid environments at producing biologically-active
substances and vaccines.
It is known the device for cultivation of microorganisms (DCM) which
contains a inclined installed on the frame with opportunity to turn round its
axis platform with pins (fingers, rods) on its butt end, located with air gap
(for shaking) between pins cylindrical in their cross-cut volume for placing of
working liquid and a drive (for example, AC of USSR ¹ 1731801, Ñ12Ì1/10, 1992)
The fault of this DCM consists in considerable level of
vibration and noise that appear in consequence of presence of air gaps between
pins of platform and volumes.
It is known the DCM which contains horizontal installed on the frame
with the possibility of turning around in vertical plate drum with longitudinal
sections and placed in sections of drum parallel to its axis cylindrical in
cross-cut volumes for placing of working liquid, and also a drive (for example
AC of USSR ¹
499293, Ñ12Â1/10, 1976).
This DCM is the nearest to the proposed engineering solution because of
its technical essence and reaching effect and is accepted as the nearest
analogue.
The fault of the known DCM consists in low effectiveness of mixing of
working liquid by the length of volumes, and so by their volume, that slows
down the growth of microorganisms and leads to the decrease of productivity.
The mentioned fault is conditioned of that the volumes for placing of
working liquid have circular cylindrical shape in their cross-cut, and that is
why they do not ensure the change of shape (and sizes) of volume of working
liquid while turning around.
In the
basis of the utility model it is putted the problem of improvement of DCM, in
which by means of introduction in the construction each of the volumes of extra
element ensures by the growth of transference of working liquid by its volume,
especially by the length of volumes, that intensifies the mass-exchange in
biomass and leads to the growth of productivity.
The putted problem is solved by that in the DCM which contains
horizontal installed on the frame with the possibility of turning around in
vertical plate drum with longitudinal sections and placed in sections of drum
volumes for placing of working liquid, and also a drive, according to proposed
utility model the new is that each volume for placing of working liquid is
equipped with joined to the bottom and side walls longitudinal dividing wall,
which is situated with air gap relative to opposed to the bottom walls of
volume and is placed in its diametrical plate.
The equipping of each volume with joined to the bottom and side walls
longitudinal dividing wall, which is situated with air gap relative to opposed
to the bottom walls of volume and is placed in its diametrical plate, ensures
the overflowing of working liquid along the volumes at turning (with
simultaneous change of its height), that provokes its extra mixing, and that
activates the growth of microorganisms and leads to the growth of productivity.
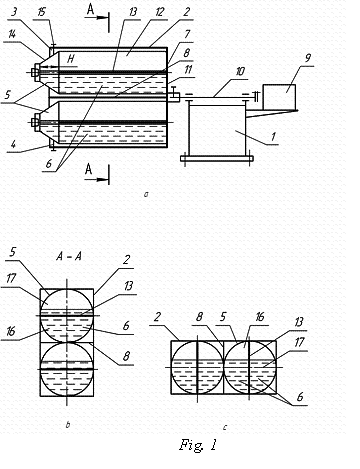
On the fig. 1, à it is schematically
presented the proposed DCM, on the fig. 1, b –crosscut A-A on the
fig. 1, à; on fig. 1, c – the change of the shape of volume of working liquid
in case of turning of drum at the angle 90°.
The DCM contains horizontal installed on the frame 1 with the
possibility to turn around its axis drum 2 with sections 3, 4, in which there
are situated volumes 5 for placing of working liquid 6. Drum 2 is carried out
in a form of opened at one end box 7 with longitudinal dividing wall 8 and
joined by bottom to the turning of drive 9 and shaft 10.bottom 11 and side
walls 12 with transversal dividing wall 13, which is placed with air gap H
relative to opposite to the bottom walls 14 volumes and is situated in its
diametrical plate. Against the axial displacement in sections 3, 4 of drum 2
the volumes 5 era fixated by elements of fixation 15.
Accept of determined on drawing, drum 2 can have another known shape and
a couple of dividing walls 8, and also inclined location (not shown).
The DCM works in next way.
 After
filling sterilized volumes 5 with working liquid 6 (nutrient liquid and sowing
material) they are locating in section 3, 4 of drum 2, fasting with fixing
elements 15 against removals and turn on the drive 9, consequently the drum 2
and the volumes 3, 4 comes into rotary movement. At the turning it happens the
transfusion of working liquid along the wallsides of volumes 3, 4, that causes,
as in the nearest analogue, its mixing. Simultaneous with the transfusion, it
happens the overflowing of working liquid because of created by dividing wall
13 air gap H from one part (compartment) of volume 5 into another, filled up
with air, part. Thus, for example, under the turning of drum 2 from the initial
(fig. 1, b) position on the angle 90° (fig. 1. c), almost half a
working liquid 6, that locates under the dividing wall 13 overflows to another
her part, from compartment 16 into compartment 17, and at another turning of
drum at the angle 90° (not
shown) – working liquid will completely fill up the compartment 17. The
overflowing of working liquid 6 to different sides of dividing wall 13, in
contrast to the nearest analogue, provokes extra mixing of along the length of
volumes 5, owing to what the intensity of mixing as liquid by itself as contacting
with it gas (air) grows up.
After
filling sterilized volumes 5 with working liquid 6 (nutrient liquid and sowing
material) they are locating in section 3, 4 of drum 2, fasting with fixing
elements 15 against removals and turn on the drive 9, consequently the drum 2
and the volumes 3, 4 comes into rotary movement. At the turning it happens the
transfusion of working liquid along the wallsides of volumes 3, 4, that causes,
as in the nearest analogue, its mixing. Simultaneous with the transfusion, it
happens the overflowing of working liquid because of created by dividing wall
13 air gap H from one part (compartment) of volume 5 into another, filled up
with air, part. Thus, for example, under the turning of drum 2 from the initial
(fig. 1, b) position on the angle 90° (fig. 1. c), almost half a
working liquid 6, that locates under the dividing wall 13 overflows to another
her part, from compartment 16 into compartment 17, and at another turning of
drum at the angle 90° (not
shown) – working liquid will completely fill up the compartment 17. The
overflowing of working liquid 6 to different sides of dividing wall 13, in
contrast to the nearest analogue, provokes extra mixing of along the length of
volumes 5, owing to what the intensity of mixing as liquid by itself as contacting
with it gas (air) grows up.
The growth of intensity of mixing (mass-exchange) leads to growth of
microorganisms that lead to the growth of productivity.