Kabatayeva R.S.*,
Rubtsova Î.À.**, Kukulin V.I.**, Zhusupov Ì.À.*
*al-Farabi Kazakh
National University, Almaty, Kazakhstan;
**D.V.Skobeltsyn Scientific Research Institute for Nuclear Physics
of M.V.Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia
Elastic scattering of a-particles
on 6Li nucleus in the three particle model
There is a consideration of a-particles scattering from weakly bound cluster nucleus  in the framework of three cluster
in the framework of three cluster  model in the present work. Continuum
model in the present work. Continuum  states are projected on the finite basis of stationary wave
packets what allows to lead the total problem of three bodies to a problem of bound channels. There are represented the calculations
results of
states are projected on the finite basis of stationary wave
packets what allows to lead the total problem of three bodies to a problem of bound channels. There are represented the calculations
results of  -scattering differential cross
sections in the framework of three particle model and comparison with other
authors.
-scattering differential cross
sections in the framework of three particle model and comparison with other
authors.
The problem about
low energy scattering of 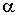 -particles on the weakly bound
-particles on the weakly bound  isotopes has a great fundamental and applied importance. From the fundamental
side the scattering in
isotopes has a great fundamental and applied importance. From the fundamental
side the scattering in  system is interesting, first of all, owing to anomalous low
binding energy of
system is interesting, first of all, owing to anomalous low
binding energy of  by
by  channel (
channel ( = 1.47 MeV), i.e. proximity to
disintegration threshold. This means the relative easiness of
= 1.47 MeV), i.e. proximity to
disintegration threshold. This means the relative easiness of  excitation into the states of
excitation into the states of  continuum in the process of interaction with incident
continuum in the process of interaction with incident  -particle. In turn, such an
excitation of
-particle. In turn, such an
excitation of  continuum leads to the great contribution of intermediate three
cluster
continuum leads to the great contribution of intermediate three
cluster  states in the scattering process at small energies. And the three cluster configurations are
virtually the excited states of
states in the scattering process at small energies. And the three cluster configurations are
virtually the excited states of  nucleus. That is why it is possible to predict the strong
transitions (for example, radiation) of
nucleus. That is why it is possible to predict the strong
transitions (for example, radiation) of  continuum states into the ground state of
continuum states into the ground state of  .
.
From the other
side such a process of a particle and weakly bound nucleus interaction is
typical for interaction of non stable (radioactive) nuclei as  and etc. with stable targets. That is why we can think that it is
better to understand the features of such interactions of the stable particle
with non stable (weakly bound) nucleus by investigation of interaction with
well investigated cluster nucleus such as
and etc. with stable targets. That is why we can think that it is
better to understand the features of such interactions of the stable particle
with non stable (weakly bound) nucleus by investigation of interaction with
well investigated cluster nucleus such as  which has an anomalous low binding energy.
which has an anomalous low binding energy.
From the applied
side, the nuclear reactions of nucleons and  -particles with
-particles with  nucleus are important for the better understanding of elements
evolution in the Big Bang and at super nova outburst. This is closely connected
to the old problem of abundance of
nucleus are important for the better understanding of elements
evolution in the Big Bang and at super nova outburst. This is closely connected
to the old problem of abundance of  isotopes in the Universe, observed in the “iron” stars, in
comparison with the predictions of the standard astrophysical models. It is clear that for sure estimations of
isotopes in the Universe, observed in the “iron” stars, in
comparison with the predictions of the standard astrophysical models. It is clear that for sure estimations of  isotopes abundance it is necessary to know as possible exact the
probability of its synthesis and its disintegration in different nuclear reactions.
And the channel
isotopes abundance it is necessary to know as possible exact the
probability of its synthesis and its disintegration in different nuclear reactions.
And the channel  is one of the main channels.
is one of the main channels.
In this work we
have investigated the role of the intermediate states of  -continuum of target nucleus
-continuum of target nucleus 
 in the process of
in the process of  -particles interaction with
-particles interaction with  nucleus. The simple general physical considerations show that
these
nucleus. The simple general physical considerations show that
these  states are to give the most contribution into the cross sections
of elastic and inelastic
states are to give the most contribution into the cross sections
of elastic and inelastic  scattering, and also into the cross sections of
scattering, and also into the cross sections of  radiation capture.
radiation capture.
Since the total
solution of scattering in  system is too tedious and time-consuming because of the big
coulomb effects, we carried out the packet reduction [1] of the problem. The
packet reduction means in our case that we projected the states of the three
particle continuum on the discrete basis of wave packets and instead of the
solution of the total three particles Schrodinger equation moved to a problem
for the coupled channel.
system is too tedious and time-consuming because of the big
coulomb effects, we carried out the packet reduction [1] of the problem. The
packet reduction means in our case that we projected the states of the three
particle continuum on the discrete basis of wave packets and instead of the
solution of the total three particles Schrodinger equation moved to a problem
for the coupled channel.
There are
represented the calculated differential cross sections in the figure.

Fig. The differential
cross sections of the elastic  -scattering: dashed curve – with the
coupling potential accounting only the ground state of
-scattering: dashed curve – with the
coupling potential accounting only the ground state of  , dotted – with the folding
potential, the solid curve – with the potential, accounting all channels of
excitation of
, dotted – with the folding
potential, the solid curve – with the potential, accounting all channels of
excitation of  in
in  continuum, the chain line – with the inverse potential [2].
continuum, the chain line – with the inverse potential [2].
In the work [2]
the differential cross sections of  scattering were found for model of potential, obtained from the
solution of the inverse scattering problem on the base of the empirical scattering
data. In work [3] the wave functions of the nucleus
scattering were found for model of potential, obtained from the
solution of the inverse scattering problem on the base of the empirical scattering
data. In work [3] the wave functions of the nucleus  in
in  model were found with the help of variation method, then these
functions were used for a construction of the folding potential, responding to
model were found with the help of variation method, then these
functions were used for a construction of the folding potential, responding to  -scattering on the nucleus
-scattering on the nucleus  , considered as a whole particle,
i.e. without accounting its internal excitations into the
, considered as a whole particle,
i.e. without accounting its internal excitations into the  continuum.
continuum.
We considered the
role of the states of the intermediate  continuum with
continuum with  in the elastic scattering of
in the elastic scattering of  -particles on the weakly bound nuclei
-particles on the weakly bound nuclei
 . For calculations in the framework
of the
. For calculations in the framework
of the  model there were used the method of the stationary wave packets and
packet reduction of the three particles scattering equations in the three cluster
system
model there were used the method of the stationary wave packets and
packet reduction of the three particles scattering equations in the three cluster
system  . We found, that the account of the
states of the intermediate continuum noticeably smoothed the sharp oscillations
of the scattering differential cross sections, typical for the folding model
potential and made the cross sections closer to the empirical cross sections of
scattering, obtained on the base of the potential of inverse problem, i.e. one
can say that the account of the intermediate continuum substantially approaches
the solution of the three particles model problem to the exact solution of
scattering problem (extracted directly from the experimental data).
. We found, that the account of the
states of the intermediate continuum noticeably smoothed the sharp oscillations
of the scattering differential cross sections, typical for the folding model
potential and made the cross sections closer to the empirical cross sections of
scattering, obtained on the base of the potential of inverse problem, i.e. one
can say that the account of the intermediate continuum substantially approaches
the solution of the three particles model problem to the exact solution of
scattering problem (extracted directly from the experimental data).
References
1. V.I. Kukulin, V.N. Pomerantsev, Î.À. Rubtsova. Theoret.Math.Phys. 150, 473 (2007).
2. R.S. Mackintosh, S.G. Cooper, V.I. Kukulin, Nucl. Phys. A 645.
399(1999).
3. S.B. Dubovichenko, Phys.Atom.Nucl. 73, 1573(2010).
![]() in the framework of three cluster
in the framework of three cluster ![]() model in the present work. Continuum
model in the present work. Continuum ![]() states are projected on the finite basis of stationary wave
packets what allows to lead the total problem of three bodies to a problem of bound channels. There are represented the calculations
results of
states are projected on the finite basis of stationary wave
packets what allows to lead the total problem of three bodies to a problem of bound channels. There are represented the calculations
results of ![]() -scattering differential cross
sections in the framework of three particle model and comparison with other
authors.
-scattering differential cross
sections in the framework of three particle model and comparison with other
authors. 