Ilyassova B.S.
The Scientific Research Institute of Cardiology and Internal Diseases of
Health Ministry of Kazakhstan
The
effect of the short course of the recombinant interleukin-2 in patients with
liver cirrhosis causes by HBV and HCV infection
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a
serious neuropsychiatric complication of both acute and chronic liver disease.
This disease encompasses a broad range of neuropsychiatric abnormalities of
varying severity: affected patients exhibit alterations in psychomotor,
intellectual, cognitive, emotional, behavioral and fine motor functions. Overt
HE (OHE) is a syndrome of neurological and neuropsychiatric abnormalities that
can be detected by bedside clinical tests. By contrast, patients with minimal
HE (MHE) present with normal mental and neurological status upon clinical
examination but specific psychometric tests yield abnormal results. According to the modern conception of the liver encephalopathy
pathogenesis the basic mechanism of its development is synergic action ammonia and inflammation, which leads
to the endotoxemia and immune paralysis [R. Prakash, K.D. Mullen, 2007, Wright G. et al, 2007]. The standard treatment of HE acts on two mechanisms of
pathogenesis of HE: ammonia and bacterial translocation leading to endotoxemia
but doesn’t act on the inflammation,
which leads to immune paralysis in patients with liver cirrhosis, determinates
severity of HE and often outcome of disease [Licinio J, Wong ML, 1997, De Vries HE et al, 1996].
The aim
of this study to compare effectiveness of antibacterial therapy with the
lactulosa and the therapy of the same drugs with the including the recombinant
interleukin-2
Material and methods:
thirty-seven non-treatment
patients with liver cirrhosis Class B
and Class C (Child-Pugh) with HE Degree I (diagnosed by
neuropsychometric test and the West Haven criteria) caused by HBV and HCV hepatitis were
included in this study as well as thirty age and sex matched healthy control.
Group A (N=19 patient) took during 10 days the ceftriaxon 2 g per day
intramuscular and lactulosa 30 ml 3 time per day. The Group B (N=18 patient) took the same drugs and Interleukin-2
(rIL2)(Ronkoleukin, Ltd Biotech,
S-Petersburg) 500 000 IU N2 1
time per 3 days intravenous in 400 ml isotonic solution. The CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD16/56+ (NK), CD25+
lymphocyte subtypes were cytometrically quantified from patients in groups A
and B and in health control group investigated (FaxCalibur, BD). Concentration
of interleukin-2 (IL-2), tumor necrosis
factor –α (TNF-α), interferon-α (INFγ) in the serum were
estimated by ELISA (IBL, Hamburg). For quantitative measuring of MHE were
included Psychometric testing NCT-A and assessment of health-related
quality of life by Questionnaire
SF-36 [Marchesini
G , 2001, Bao ZJ, 2007
]. The SF-36 is a generic HRQL instrument measuring
8 dimensions: 23 “Physical Functioning” (PF),
“Role Physical”(RP), “Bodily
Pain” (BP), “General Health” (GH) “Vitality” (VT), “Social Functioning” (SF),
“Role Emotional” (RE), and “Mental Health” (MH) Items are transformed
into scores from 0 (worst) to 100 (best possible health state).
The results: The dates of research before treatment were not significant different in
both Groups. The amount of the subset of lymphocytes and dates of cytokines in
serum for both groups: CD3+lymphocytes 870±46/ml, CD4+
465±61/ml, CD8+
471±29/ml, NK 280±36/ml, CD25+ 190±54/ml, the
level of IL2 0,5±0,1 pg/ml, INF-γ 16,2±3,6 pg/ml, TNF-α 182,5 ±75,1
pg/ml. The results of psychometric testing for both Groups: NCT-A
65±8 seconds, PF 32,2±3,9%,
RP 52±3,2 %, BP 48±4,1%, GH
68±5,0%, VT 56±4,1%, SF 20±3,1%,
RE 48±4,2%, MH 44±2,9%. The results of the study after treatment
have showed, that the amount of subpopulation of lymphocytes and the levels of
cytokines not significant change in Group A: CD3+ (882±76)/ml (Ð![]() 0,5), CD4+ (457±71)/ ml (Ð
0,5), CD4+ (457±71)/ ml (Ð![]() 0,5), CD8+ (478±27)/ ml (Ð
0,5), CD8+ (478±27)/ ml (Ð![]() 0,5), NK (284±41)/ml (Ð
0,5), NK (284±41)/ml (Ð![]() 0,5), CD25+ (186±60)/ ml (Ð
0,5), CD25+ (186±60)/ ml (Ð![]() 0,5), IL2 (0,41±0,16) pg/ml (Ð
0,5), IL2 (0,41±0,16) pg/ml (Ð![]() ,5), INFγ (19,2±3,6) pg/ml (Ð<0,05), TNFα (176,8 ±65,6) pg/ml (Ð
,5), INFγ (19,2±3,6) pg/ml (Ð<0,05), TNFα (176,8 ±65,6) pg/ml (Ð![]() 0,5). Including to HE treatment of recombinant
interleukin-2 significant improved the dates of immunity : CD 3+ (989 ±44,1)/ml (Ð<0,05), CD 4+ (650±24,7)/ml (Ð<0,05), CD8+ (330±64,4)/ml (Ð<0,05),
NK(470±34,9)/ml(Ð<0,05),
CD25+(128±36,1)/ml (Ð<0,05). IL2 (38,1±14,1) pg/ml(Ð<0,001), INFγ (96 ±12,2) pg/ml
(Ð<0,001), TNF-α (78,7±34,1) pg/ml (Ð<0,001).
0,5). Including to HE treatment of recombinant
interleukin-2 significant improved the dates of immunity : CD 3+ (989 ±44,1)/ml (Ð<0,05), CD 4+ (650±24,7)/ml (Ð<0,05), CD8+ (330±64,4)/ml (Ð<0,05),
NK(470±34,9)/ml(Ð<0,05),
CD25+(128±36,1)/ml (Ð<0,05). IL2 (38,1±14,1) pg/ml(Ð<0,001), INFγ (96 ±12,2) pg/ml
(Ð<0,001), TNF-α (78,7±34,1) pg/ml (Ð<0,001).
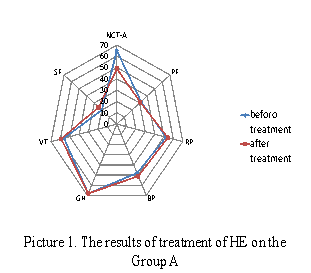
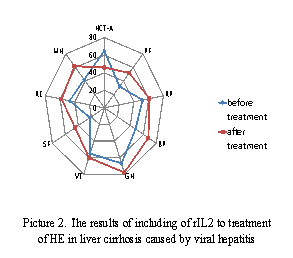
The psychometric test NCT-A in Group A showed significant improved 49±6
sec (Ð<0,05). However the results of Questionnaire
SF-36 in this Group were not significant higher after treatment (Ð![]() 0,5) (Picture 1). In the Group B
both the dates of NCT-A and of SF-36
were significant better after treatment (46±4 sec (Ð<0,05), PF – 52±2,9%,
RP – 61±3,2 %, BP – 68±4,9%, GH – 68±5,1%, VT – 58±3,0%, SF – 45±3,3%, RE – 54±4,0%, MH – 62±3,1%, (Ð<0,05). Moreover, were found direct correlation between the level of
the TNFα and the date of the MH (r=0,49) in Group B after treatment.
0,5) (Picture 1). In the Group B
both the dates of NCT-A and of SF-36
were significant better after treatment (46±4 sec (Ð<0,05), PF – 52±2,9%,
RP – 61±3,2 %, BP – 68±4,9%, GH – 68±5,1%, VT – 58±3,0%, SF – 45±3,3%, RE – 54±4,0%, MH – 62±3,1%, (Ð<0,05). Moreover, were found direct correlation between the level of
the TNFα and the date of the MH (r=0,49) in Group B after treatment.
Conclusion. Including of short
course of rIL-2 to the complex treatment of liver cirrhosis caused by viral
hepatitis regularizes endogenous production of cytokines, reduces
proinflammatory cytokine TNFα, raises the amount of immune cells in serum
and finally to removal the statement of
immune insufficiency. As confirm the NCT-A and SF-36 the effects of rIL2 on the
immune system in liver cirrhosis drive to increasing the effectiveness of
antibiotic and lactulosa, to reduction of tiredness, weakness, to decreasing of
the level of endotoxemia of brain and
to rise of capacity of work.